Modern Scripting with TypeScript: Development Tools Configuration

Visual Studio Code is by far the most used editor for TypeScript. It provides smart code completion and type checking as well as extensions and debugging tools.
We discussed on the previous article how you can use alternative runtimes to run you scripts without compilation, but in order to profit from the benefits of TypeScript such as type safety, you will have to configure your workspace with a tsconfig.json file.
To follow the next sections, Node.js (with npm included) is required. You can download the latest version from the following link.
You scripts workspace could look like the following:
├── package.json
├── tsconfig.json
├── scripts/
└── script1.ts
└── script2.tsThe source code of the workspace used on the following sections is available here.
Some dependencies are required to specify the version of Node.js (@types/node) as well as to provide a base configuration for TypeScript (@tsconfig/node24). Deno was used as a runtime for TypeScript without compilation.
The following package.json lists all these development dependencies:
{
"type": "module",
"devDependencies": {
"@tsconfig/node24": "^24.0.1",
"@types/node": "^24.10.1",
"deno": "^2.5.6"
}
}You can install the development dependencies with: npm install
Some configurations (standard libraries, module system) for TypeScript were provided by the base tsconfig @tsconfig/node24/tsconfig.json, which is based on the latest LTS version of Node.js
{
"extends": "@tsconfig/node24/tsconfig.json",
"compilerOptions": {},
"include": ["scripts/", "tmp/"],
"exclude": ["node_modules", "**/node_modules/*"]
}Other base configurations for tsconfig.json available here.
You can specify in the include array the directories that will contain TypeScript code.
For example, the scripts and tmp directory were included.
If you need to add some assets that may conflict with TypeScript, you can add them to the exclude array.
A repository was provided earlier to showcase a typical set up for a scripting workspace with TypeScript.
├── .data/
└── articles.json
├── .vscode/
└── launch.json
├── scripts/
└── export-articles-sorted-by-modified-date-desc.ts
└── types.d.ts
├── package.json
├── tsconfig.jsonYou can open the project using VS code.
Open scripts/export-articles-sorted-by-modified-date-desc.ts, then from the left sidebar select Run and Debug.
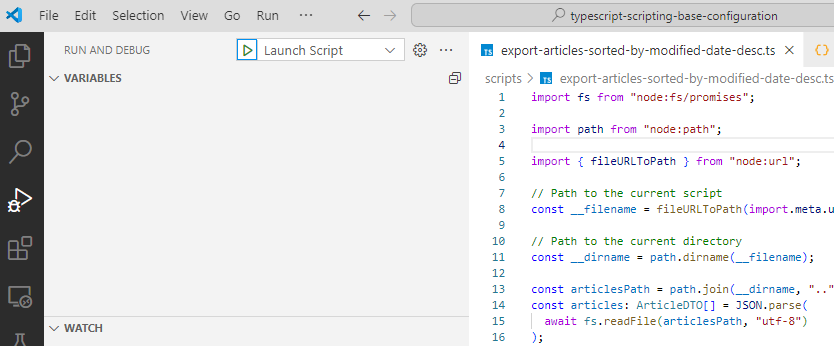
You can add a breakpoint on any line with a valid TypeScript/JavaScript instruction: click on the space to the left of the line number, a red dot will appear indicating the presence of a breakpoint. If you don't add any breakpoint the script will run without debugging.
Click on the play icon to the left of Launch Script to run and debug.
.vscode/launch.json contains the configuration necessary to run and debug any selected TypeScript file.
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"request": "launch",
"name": "Launch Script",
"type": "node",
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"env": {},
"runtimeExecutable": "deno",
"runtimeArgs": ["run", "--inspect-wait", "--allow-all"],
"attachSimplePort": 9229
}
]
}